MGEX Metadata
Satellite Metadata
Satellite metadata are vital for accurate modeling of GNSS data. These include unique identifiers like SVN, COSPAR ID, Satellite Catalog Number (NORAD ID); PRN/SVN mapping; SVN/frequency channel mapping for GLONASS; satellite mass; center of mass; transmit antenna and laser retroreflector array eccentricities; and transmit power. More details on this topic are given in the IGS white paper on satellite and operations information for generation of precise GNSS orbit and clock products.
Metadata for Galileo, QZSS, and BeiDou have already been published by the European GNSS Service Center, the Cabinet Office (CAO), Government of Japan and the China Satellite Navigation Office (CSNO). CAO also provides operational history information including orbit maintenance maneuvers and attitude switches.
- Current release of the IGS satellite metadata file
CAVE:
- releases prior to igs_metadata_2031.snx had an erroneous width of the frequency channel number (A4 instead of A3).
- different types of BDS-3 SECM satellites (A/B) have been introduced in release 2110.
Satellite metadata format description
In order to be able to store and exchange the GNSS satellite metadata in a standardized format, an extension of the solution independent exchange (SINEX) format. The version 1.00 of this format was approved by the IGS Governing Board in December 2022:
- Steigenberger P, Montenbruck O. (2022) IGS Satellite Metadata File Description, Version 1.00, doi: 10.57677/metadata-sinex
References
- Cabinet Office (2017a) QZS-1 satellite information. Tech. Rep. SPI_QZS1, Government of Japan, National Space Policy Secretariat, latest version available at https://qzss.go.jp/en/technical/qzssinfo/index.html
- Cabinet Office (2018a) QZS-2 satellite information. Tech. Rep. SPI-QZS2_B, Government of Japan, National Space Policy Secretariat, latest version available at https://qzss.go.jp/en/technical/qzssinfo/index.html
- Cabinet Office (2018b) QZS-3 satellite information. Tech. Rep. SPI-QZS3_A, Government of Japan, National Space Policy Secretariat, latest version available at https://qzss.go.jp/en/technical/qzssinfo/index.html
- Cabinet Office (2018c) QZS-4 satellite information. Tech. Rep. SPI-QZS4_B, Government of Japan, National Space Policy Secretariat, latest version available at https://qzss.go.jp/en/technical/qzssinfo/index.html
- Cabinet Office (2018d) The history information of QZS-1 operation. Tech. Rep. OHI-QZS1, Government of Japan, National Space Policy Secretariat, latest version available at https://qzss.go.jp/en/technical/qzssinfo/index.html
- Cabinet Office (2018e) The history information of QZS-2 operation. Tech. Rep. OHI-QZS2, Government of Japan, National Space Policy Secretariat, latest version available at https://qzss.go.jp/en/technical/qzssinfo/index.html
- Cabinet Office (2018f) The history information of QZS-3 operation. Tech. Rep. OHI-QZS3, Government of Japan, National Space Policy Secretariat, latest version available at https://qzss.go.jp/en/technical/qzssinfo/index.html
- Cabinet Office (2018g) The history information of QZS-4 operation. Tech. Rep. OHI-QZS4, Government of Japan, National Space Policy Secretariat, latest version available at https://qzss.go.jp/en/technical/qzssinfo/index.html
- Czopek F, Shollenberger S (1993) Description and performance of the GPS Block I and II L-band antenna and link budget. In: Proceedings of ION GPS 1993, Salt Lake City, UT, pp 37-43
- Fatkulin R, Kossenko V, Storozhev S, Zvonar V, Chebotarev V (2012) Glonass space segment: satellite constellation, Glonass-M and Glonass-K spacecraft main features. In: ION GNSS 2012, Nashville, TN, pp 3912-3930
- Hegarty C (2017) The Global Positioning System (GPS). In: Teunissen P, Montenbruck O (eds) Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems, Springer, chap 7, pp 197-218, DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-42928-1_7
- Kramer HJ (2002) Observation of the Earth and Its Environment: Survey of Missions and Sensors, 4th edn. Springer, DOI 10.1007/978-3-642-56294-5
- Montenbruck O (2017) IGS White Paper on Satellite and Operations Information for Generation of Precise GNSS Orbit and Clock Products. Version 2017/10/21, IGS Multi-GNSS Working Group. https://files.igs.org/pub/resource/working_groups/multi_gnss/Whitepaper_SatelliteMetaData_IGS_171021.pdf
- Montenbruck O, Schmid R, Mercier F, Steigenberger P, Noll C, Fatkulin R, Kogure S, Ganeshan A (2015) GNSS satellite geometry and attitude models. Advances in Space Research 56(6):1015-1029, DOI 10.1016/j.asr.2015.06.019
Montenbruck O and Steigenberger P (2020) IGS White Paper on Satellite and Operations Information for Generation of Precise GNSS Orbit and Clock Products. Version 2020/02/04, IGS Multi-GNSS Working Group, https://files.igs.org/pub/resource/working_groups/multi_gnss/Whitepaper_SatelliteMetaData_IGS_200204.pdf - Revnivykh S, Bolkunov A, Serdyukov A, Montenbruck O (2017) GLONASS. In: Teunissen P, Montenbruck O (eds) Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems, Springer, chap 8, pp 219-245, DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-42928-1_8
- Sosnica K, Thaller D, Dach R, Steigenberger P, Beutler G, Arnold D, Jäggi A (2015) Satellite laser ranging to GPS and GLONASS. Journal of Geodesy 89(7):725-743, DOI 10.1007/s00190-015-0810-8
- Steigenberger P, Thoelert S, Montenbruck O (2018) GNSS satellite transmit power and its impact on orbit determination. Journal of Geodesy 92(6):609-624, DOI 10.1007/s00190-017-1082-2
- Xu X, Li M, Li W, Liu J (2018) Performance analysis of BeiDou-2/BeiDou-3e combined solution with emphasis on precise orbit determination and precise point positioning. Sensors 18(1):135, DOI 10.3390/s18010135
- Zandbergen R, Navarro D (2008) Specification of Galileo and GIOVE space segment properties relevant for satellite laser ranging. Tech. Rep. ESA-EUING-TN/10206, iss. 3.2, 08/05/2008, ESA/ESOC, Darmstadt
- Zhao Q, Wang C, Guo J, Wang B, Liu J (2018) Precise orbit and clock determination for BeiDou-3 experimental satellites with yaw attitude analysis. GPS Solutions 22:4, DOI 10.1007/s10291-017-0673-y
Satellite Identifier
The SATELLITE/IDENTIFIER block contains only unique information that does not require a validity interval. It supersedes the existing SATELLITE/ID block: the time-dependent PRN assignment has been moved to the new SATELLITE/PRN block, Satellite Catalog Numbers (aka NORAD-ID) and a comment field have been added, and new block names have been defined (old block names denote ANTEX antenna type!). The comment field contains the launch date and common name of the satellite if available.
Satellite PRN Assignment
The SATELLITE/PRN block supersedes the existing SATELLITE/ID block. It only contains the mapping between pseudo-random noise (PRN) number and space vehicle number (SVN).
GLONASS Frequency Channel
The SATELLITE/FREQUENCY_CHANNEL block provides the mapping between SVN and frequency channels of the GLONASS frequency devision multiple access (FDMA) technology.
Satellite Mass
A mass history is currently provided for selected Galileo and all QZSS satellites.
Satellite Center of Mass
The values refer to agreed-upon origin (e.g., origin of mechanical reference system defined by manufacturer). The use of zero values if no CoM location is available is possible but deprecated.
Satellite Eccentricity
The SATELLITE/ECCENTRICITY block provides equipment locations for use in measurement modeling (antennas, retro-reflectors, etc.). The values refer to an agreed-upon origin (e.g., origin of mechanical reference system defined by manufacturer) and IGS conventions for orientation of spacecraft body axes. The same origin applies for all devices and the center-of-mass of a given satellite. Users and providers are responsible to ensure the consistency of SATELLITE/ECCENTRICITY and SATELLITE/COM blocks.
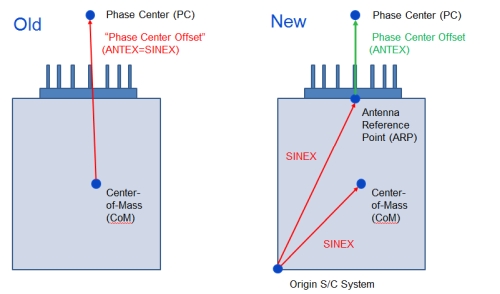
Current ANTEX conventions imply the use of the center-of-mass as “reference point” for GNSS antennas (old in the above figure). This convention must be retained for SINEX up to the release of new ANTEX format. The definition of block-specific antenna reference points is encouraged for all GNSSs (new in the above figure). These are already available for Galileo IOV and FOC. The GNSS antenna names in the current IGS metadata SINEX file must match those in rcv_ant.tab for consistency with the current ANTEX file. New names should be defined when transitioning to mechanically defined antenna reference points. A list of old and new GNSS device names is given below. CAVE: Antenna names are different from block names! In version 1.4 of the ANTEX format, there are no entries for multiple L-band antennas as already employed on, e.g. GLO-K1 (R801) and QZSS.
Current (ANTEX 1.4 compatible)
Future (antenna and LRA reference points)
The technique-specific observation type indicator (T) is P for GNSS and L for SLR. Current SLR eccentricities refer to the “phase center”. This has to be replaced by the reference point for use with nadir-angle dependent range correction.
Satellite Transmit Power
Satellite transmit power is needed for the computation of antenna thrust. The transmit power values for QZSS are provided by the manufacturer, whereas the other values originate from high-gain antenna measurements.
Block and Device Names
GNSS block and device names
The old GNSS device names are compatible with the current ANTEX file. New device names are proposed along with a new version of the ANTEX format to support multiple GNSS antennas on a single GNSS satellite like GLO_K1A and the different QZSS satellites.
| Block | Device Name GNSS old |
Device Name GNSS new |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS-I | BLOCK I | LANT_GPS_I | GPS Block I |
| GPS-II | BLOCK II | LANT_GPS_II | GPS Block II |
| GPS-IIA | BLOCK IIA | LANT_GPS_IIA | GPS Block IIA |
| GPS-IIR-A | BLOCK IIR-A | LANT_GPS_IIR-A | GPS Block IIR (original antenna) |
| GPS-IIR-B | BLOCK IIR-B | LANT_GPS_IIR-B | GPS Block IIR (new antenna) |
| GPS-IIR-M | BLOCK IIR-M | LANT_GPS_IIR-M | GPS Block IIR-M |
| GPS-IIF | BLOCK IIF | LANT_GPS_IIF | GPS Block IIF |
| GPS-III | BLOCK IIIA | LANT_GPS_III | GPS Block III |
| GLO | GLONASS | LANT_GLO | GLONASS |
| GLO-M | GLONASS-M | LANT_GLO_M | GLONASS-M+ |
| GLO-M+ | GLONASS-M | LANT_GLO_M+ | GLONASS-M |
| GLO-K1A | GLONASS-K1 | LANT_GLO_K1A | GLONASS-K1 |
| L3ANT_GLO_K1A | |||
| GLO-K1B | GLONASS-K1 | LANT_GLO_K1B | GLONASS-K1 |
| GAL-0A | GALILEO-0A | LANT_GIOVEA | GIOVE-A |
| GAL-0B | GALILEO-0B | LANT_GIOVEB | GIOVE-B |
| GAL-1 | GALILEO-1 | LANT_GAL_1 | Galileo IOV |
| GAL-2 | GALILEO-2 | LANT_GAL_2 | Galileo FOC |
| BDS-2M | BEIDOU-2M | LANT_BDS_2M | BeiDou-2 MEO |
| BDS-2I | BEIDOU-2I | LANT_BDS_2I | BeiDou-2 IGSO |
| BDS-2G | BEIDOU-2G | LANT_BDS_2G | BeiDou-2 GEO |
| BDS-3SI-CAST | BEIDOU-3SI-CAST | LANT_BDS_3SI_CAST | BeiDou-3 experimental IGSO, CAST |
| BDS-3SI-SECM | BEIDOU-3SI-SECM | LANT_BDS_3SI_SECM | BeiDou-3 experimental IGSO, CAS |
| BDS-3SM-CAST | BEIDOU-3SM-CAST | LANT_BDS_3SM_CAST | BeiDou-3 experimental MEO, CAST |
| BDS-3SM-SECM | BEIDOU-3SM-SECM | LANT_BDS_3SM_SECM | BeiDou-3 experimental MEO, CAS |
| BDS-3M-CAST | BEIDOU-3M-CAST | LANT_BDS_3M_CAST | BeiDou-3 MEO, CAST |
| BDS-3M-SECM-A | BEIDOU-3M-SECM | LANT_BDS_3M_SECM_A | BeiDou-3 MEO, SECM (original bus) |
| BDS-3M-SECM-B | LANT_BDS_3M_SECM_B | BeiDou-3 MEO, SECM (new bus) | |
| BDS-3G | BEIDOU-3G | LANT_BDS_3G | BeiDou-3 GEO |
| BDS-3I | BEIDOU-3I | LANT_BDS_3I | BeiDou-3 IGSO |
| QZS-1 | QZSS | LANT_QZS_1 | QZSS Block I |
| L1SANT_QZS_1 | |||
| QZS-2I | QZSS-2I | LANT_QZS_2I | QZSS Block II IGSO |
| L1SANT_QZS_2I | |||
| L5SANT_QZS_2I | |||
| QZS-2G | QZSS-2G | LANT_QZS_2G | QZSS Block II GEO |
| L1SANT_QZS_2G | |||
| L5SANT_QZS_2G | |||
| QZS-2A | QZSS-2A | LANT_QZS_2A | QZSS Block IIA |
| L1SANT_QZS_2A | |||
| L5SANT_QZS_2A | |||
| IRS-1I | IRNSS-1I | LANT_IRNSS_1I | NAVIC IGSO |
| IRS-1G | IRNSS-1G | LANT_IRNSS_1G | NAVIC GEO |
SLR retroreflector device names
| LRA name | Description |
|---|---|
| LRA_GPS_IIA | GPS IIA satellites |
| LRA_GPS_IIIF | GPS IIIF satellites |
| LRA_GLO_396_AL | GLONASS sats, 396 prisms (irreg. planar, Al coating) |
| LRA_GLO_132_AL | GLONASS sats, 132 prisms (irreg. circle, Al coating) |
| LRA_GLO_M_AL | GLONASS-M sats, 112 prisms and Al coating |
| LRA_GLO_M | GLONASS-M sats, 112 prisms (uncoated) |
| LRA_GLO_K1 | GLONASS-K1 sats, 123 prisms (ring array, uncoated?) |
| LRA_GIOVEA | GIOVE-A LRA, 76 prisms |
| LRA_GIOVEB | GIOVE-B LRA, 67 prisms |
| LRA_GAL_1 | Galileo IOV satellites, 84 prisms |
| LRA_GAL_2 | Galileo FOC satellites, 60 prisms |
| LRA_BDS_2M | BeiDou-2 MEO satellites, 42 prisms |
| LRA_BDS_2GI | BeiDou-2 GEO and IGSO satellites, 90 prisms |
| LRA_BDS_3SM | BeiDou-3S MEO satellites (same as BDS_2M?) |
| LRA_BDS_3SI | BeiDou-3S IGSO satellites (same as BDS_2GI?) |
| LRA_BDS_3M | BeiDou-3 MEO satellites (same as BDS_3M?) |
| LRA_BDS_3GI | BeiDou-3 GEO and IGSO satellites (same as BDS_2GI?) |
| LRA_QZSS_1 | QZS-1 (QZSS Block I) satellite, 56 prisms (uncoated) |
| LRA_QZSS_2 | QZS-2 (QZSS Block II GEO & IGSO), 56 prisms (coated) |
| LRA_IRNSS | IRNSS satellites, 40 prisms |
Last Updated on 15 Dec 2022 12:57 UTC

